CLASS-7
CUBE ROOT
CUBE ROOT -
A cube root is a special value that, when we multiply three times, gives us the desired number. Thus, a perfect cube is a cube of a whole number.
A cube root of a number x is a value that, when multiplied by itself three times, gives x. It is denoted as ∛x.
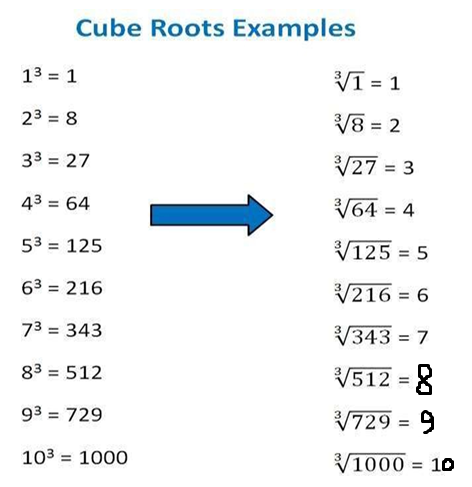
A cube root is a special value that, when we multiply three times, gives us the desired number. Thus, a perfect cube is a cube of a whole number. Cube root is the inverse process of calculating the cube of a number. It is denoted by the symbol ‘∛’. Let us see some examples here now.
To find the cube root of a nunumber 7, we want a number which when multiplied thrice with itself shall give 27. We can write,
27 = 3 × 3 × 3 = 3³
Taking cubic root on both the sides; or ∛27 = ∛3³
Therefore, the cube-root of 27 is 3.
Please note that we will only consider the positive values cube roots of the natural numbers.
For Example:-
- ∛27 = 3 because 3 × 3 ×3 = 3³= 27.
- ∛8 = 2 because 2 × 2 × 2 = 2³= 8.
- ∛125 = 5 because 5 × 5 × 5 = 5³= 125.
- ∛−64 = −4 because −4 × −4 × −4 = (-4)³= −64.
- ∛2 ≈ 1.2599 (since 2 is not a perfect cube, its cube root is an irrational number).

Some Other Way Of Understanding Cube Root:-
1. Volume Perspective (Geometric Interpretation):-
Imagine you have a cube with a total volume of x. The cube root of x tells you the length of each side of the cube.
- Example:- If the volume is 27 cubic units, then the side length is 3 units because 3 × 3 × 3 = 27.
2. Repeated Multiplication:-
The cube root of a number is the value that you multiply by itself three times to get the original number.
- Example:- ∛64 = 4 because 4 × 4 × 4 = 4³ = 64 and ∛64 = ∛4³= 4
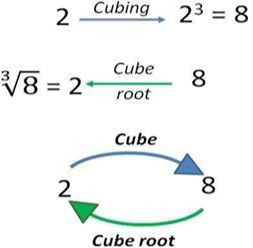
3. Inverse of Cubing:-
Just like squaring and square roots are inverse operations, cubing and cube roots undo each other:
- 2³ = 8 → ∛8 = ∛2³= 2
- 5³ = 125 → ∛125 = ∛5³ = 5
4. Graphical Understanding:-
If you graph y = x³, the cube root is just moving backward along that curve. Unlike square roots, cube roots can be negative:
- ∛−8 = −2 because (−2) × (−2) × (−2) = −8.
5. Real-Life Example:-
Think about a sugar cube or a Rubik’s Cube:- If you know the total number of smaller cubes inside, the cube root tells you how many cubes line up along each edge.