CLASS-7
PROPERTIES OF SUBTRACTION OF INTEGERS
PROPERTIES OF SUBTRACTION OF INTEGERS -
The properties of subtraction of integers are slightly different from addition because subtraction is not always commutative or associative. Here are the key properties:
1. Closure Property (Not Always True):-
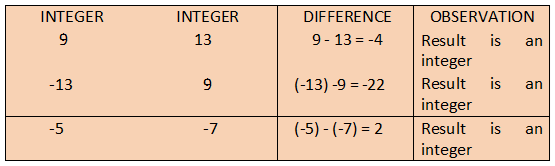
- Definition: The result of subtracting two integers is always an integer.
- Example: 5 − 3 = 2 (which is an integer).
- Exception: Unlike addition, subtraction does not always produce a positive result. For example, 3 − 5 = −2, but it is still an integer.
Thus, we find that the difference of two integers is an integer. In other words,
If ‘a’ and ‘b’ are any two integers, then a - b is also an integer.
2. Non-Commutative Property:-
- Definition: Changing the order of integers in subtraction changes the result.
- Example: 7 − 4 ≠ 4 − 7 (since 7 − 4 = 3 but 4 − 7 = −3).
- Consider the integers 7 and (-4).
We note that 7 - (-4) = 7 + 4 = 11 and (-4) - 7 = -11
→ 7 - (-4) ≠ (-4) - 7.
Thus, we conclude that subtraction is not commutative for integers i.e if ‘a’ and ‘b’ are any two integers, then a - b ≠ b - a,
So, a ≠ b.
3. Non-Associative Property:-
- Definition: The way integers are grouped in subtraction affects the result.
- Consider the integers 3, -5 and 11.
We note that (3 - (-5)) - 11 = 8 - 11 = -3 and 3 - ((-5) - 11) = 3 - (-16) = 3 + 16 = 19
→ (3 - (-5)) - 11 ≠ 3 - ((-5) - 11).
- Example: (8 − 3) − 2 ≠ 8 − (3 − 2).
(8 - 3) - 2 = 5 - 2 = 3 and 8 − (3 − 2) = 8 − 1 = 7.
→ (8 - 3) - 2 ≠ 8 - (3 - 2)
Thus,we conclude that subtraction is not associative for integers i.e if a, b and c are any integers,then (a - b) - c ≠ a - (b - c), and c ≠ 0.
4. Identity Property:-
- Definition: Subtracting 0 from any integer does not change its value.
- Example: 6 − 0 = 6.
5. Subtraction as Addition of the Opposite:-
- Definition: Subtraction can be rewritten as the addition of the additive inverse.
- Example: 5 − 8 = 5 + (−8) = −3.