CLASS-8
PYTHAGORAS THEOREM - PROBLEM & SOLUTION
There are some example are given below for your better understanding and all these example may help you to solve the other type of problem on basics of Pythagoras Theorem.
Example.1) Calculate the length of the unknown side in each of the following triangles
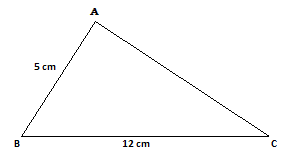
Ans.) As per the Pythagoras theorem AC² = AB² + BC²
As per the above given picture AB = 5 cm and BC = 12 cm
So, AC² = 5² + 12² = 25 + 144 = 169
Or, AC = √169 = √13² = 13 (Ans.)
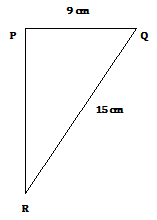
Ans.) As per the Pythagoras theorem QR² = PQ² + RP²
As per the above given picture PQ = 9 cm and QR = 15 cm
So, 15² = 9² + PR²
Or, PR² = 15²- 9²
Or, PR² = 225 – 81 = 144
Or, PR = √144 = √12² = 12 (Ans.)
Example.2) Calculate the length of BC in the adjoining figure. Is ∆ ABD is a right angled triangle ?
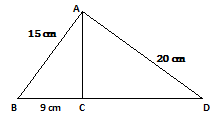
Ans.) In ∆ ABC, AB² = AC²+ BC², by Pythagoras theorem
Here from the above given picture we can find, AB = 15 cm, BC = 9 cm
So, AB² = AC² + BC²
Or, 15² = AC² + 9²
Or, 225 = AC² + 81
Or, AC² = 225 – 81 = 144
Or, AC = √144 = √12² = 12 cm
Now, in ∆ ACD, AD² = AC² + CD², by Pythagoras theorem
Here we can find from the above given picture, AC = 12 cm, AD = 20 cm.
So, AD² = AC² + CD²
Or, 20² = 12² + CD²
Or, 400 = 144 + CD²
Or, CD² = 400 – 144 = 256
Or, CD = √256 = √16² = 16 cm
Now, BD = BC + CD
Or, = 9 + 16 = 25
We can observe that, BD² = AB² + AD²
= 15² + 20² = 225 + 400 = 625
BD = √625 = √25² = 25
In, ∆ ABD is a right angled triangle in which BD is the hypotenuse, that is, √A = 90⁰ (Ans.)
Example.3) Find PQ in the following figure.
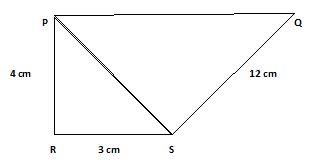
Ans.) In the right angled ∆ PRS, PS² = PR² + RS², from the above given picture we can find -
PR = 4 cm, and RS = 3 cm
Or, PS² = 4² + 3² = 16 + 9 = 25
Or, PS = √25 = √5² = 5 cm
In the right angled ∆ PRS, PQ² = PS² + SQ², from the above given picture we can find -
PS = 5 cm, and SQ = 12 cm
Or, PQ² = 5² + 12² = 25 + 144 = 169
Or, PQ = √169 = √13² = 13 cm
So, we can find that, PQ = 13 cm (Ans.)
Example.4) Calculate ‘x’ in below figure
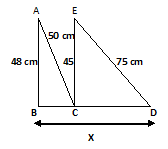
Ans.) In ∆ ABC, AC² = AB²+ BC², by Pythagoras theorem
From above given picture, AB = 48 cm, and AC = 50 cm
So, AC² = AB² + BC²
Or, 50² = 48² + BC²
Or, BC² = 50² - 48²
= 2500 – 2304 = 196
Or, BC² = 196
Or, BC = √196 = √14² = 14
Now, in ∆ ECD, ED² = EC²+ CD², by Pythagoras theorem
From the above given picture, ED = 75 cm, and EC = 45 cm
So, ED² = EC² + CD²
Or, 75² = 45² + CD²
Or, 5625 = 2025 + CD²
Or, CD² = 5625 – 2025 = 3600
Or, CD = √3600 = √60² = 60
Now, as we can find from the above picture, x = BC + CD
Here we find, BC = 14 cm, and CD = 60 cm.
Now, x = BC + CD = 14 + 60 = 74 cm
So, the desired answer is 74 cm (Ans.)