CLASS-9
TRIGONOMETRICAL RATIOS - PROBLEM & SOLUTION
Example.1) In △ABC in which ∠B = 90⁰, AB = 5 units and AC = 13 units, calculate –
(i) sin A
(ii) tan A
(iii) cosec² A - cot² A
(iv) cos C
(v) cot C
(vi) cosec C
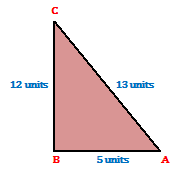
Ans.) By Pythagoras theorem, we have –
BC = √(AC² - AB²) = √(13² - 5²) = √169 – 25
= √144 = √12²
= 12 cm
For ∠A, we have –
Base = AB, Perpendicular = BC, and Hypotenuse = AC
Perpendicular BC 12
(i) sin A = --------------- = -------- = -------
Hypotenuse AC 13
Perpendicular BC 12
(ii) tan A = ---------------- = ------- = ------
Base AB 5
1 13 1 5
(iii) cosec A = ------- = ------- and cot A = ------- = ------
sin A 12 tan A 12
13 5
so, (cosec² A - cot² A) = {(------)² - (------)²}
12 12
(169 – 25) 144
= ------------ = ------- = 1
144 144
For, ∠C, we have –
Base = BC = 12 units, Perpendicular = AB = 5 units, and Hypotenuse = AC = 13 units
Base BC 12
(iv) cos C = ------------- = -------- = -------
Hypotenuse AC 13
Base BC 12
(v) cot C = -------------- = ------- = -------
Perpendicular AB 5
Hypotenuse AC 13
(vi) cosec C = ---------------- = --------- = -------
Perpendicular AB 5
3
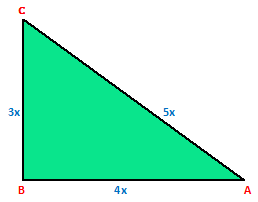
Example.2) In a right △ABC, if ∠A is acute and tan A = ------,
4
find the remaining trigonometric ratios of ∠A.
Ans.) Consider a △ABC in which ∠B = 90⁰
For ∠A, we have –
BC = AB, Perpendicular = BC, and Hypotenuse = AC
Perpendicular 3
ten A = --------------- = -------
Base 4
BC 3
= ------- = ------
AB 4
Let, BC = 3x units and AB = 4x units
Then, AC = √(AB² + BC²)
= √{(4x)² + (3x)²} = √25x² = 5x units
Perpendicular BC 3x 3
Now, sin A = --------------- = -------- = ------ = ------
Hypotenuse AC 5x 5
Base AB 4x 4
cos A = ------------- = ------- = ------- = ------
Hypotenuse AC 5x 5
1 1 5
cosec A = ---------- = -------- = -------
sin A 3/5 3
1 1 5
sec A = ---------- = -------- = -------
cos A 4/5 4
1 1 4
cot A = ---------- = -------- = ------- (Ans.)
tan A 3/4 3
√3
Example.3) If θ is an acute angle such that sin θ = -------,
2
then find the value of (cosec θ + cot θ)
Ans.) Consider a △ABC in which ∠A = θ⁰, ∠B = 90⁰
Then, Base = AB, Perpendicular = BC, and Hypotenuse = AC
Perpendicular BC √3
sin θ = ----------------- = -------- = -------
Hypotenuse AC 2
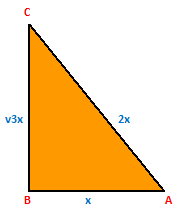
Let, Perpendicular = BC = √3x and Hypotenuse = AC = 2x
So, Base = AB = √(AC² – BC²)
= √{(2x)²- (√3x)²}
= √(4x² - 3x²)
= √x² = x
Hypotenuse AC 2x 2
cosec θ = --------------- = -------- = ------- = -------
Perpendicular BC √3x √3
Base AB x 1
cot θ = -------------- = ------- = ------- = ------
Perpendicular BC √3x √3
2 1 3
(cosec θ + cot θ) = (------ + ------) = ------ = √3 (Ans.)
√3 √3 √3
8 sin θ – 3 cos θ
Example.4) If 8 tan θ = 6, then find the value of (----------------)
8 sin θ + 3 cos θ
Ans.) If, 8 tan θ = 6
6
Then, tan θ = -------
8
sin θ
8 (---------) - 3
8 sin θ – 3 cos θ cos θ
Now, (----------------) = [------------------------]
8 sin θ + 3 cos θ sin θ
8 (---------) + 3
cos θ
8 tan θ – 3 sin θ
= ---------------- [ tan θ = -------- ]
8 tan θ + 3 cos θ
Replacing the value of tan θ, and we get –
6
8 X ------ - 3
8
= ---------------------
6
8 X ------ + 3
8
6 – 3 3 1
= ---------- = ------- = ------- (Ans.)
6 + 3 9 3
Example.5) If, sin θ + cosec θ = 5, find the value of (sin² θ + cosec² θ)
Ans.) sin θ + cosec θ = 5
=> (sin θ + cosec θ)² = 5² [squaring both the side]
=> sin² θ + cosec² θ + 2 . sin θ . cosec θ = 25
[applying (a + b)² = a² + b² + 2ab ]
1
=> sin² θ + cosec² θ + 2 . sin θ. ------- = 25
sin θ
1[ As we know, cosec θ = -------- ]
sin θ
=> sin² θ + cosec² θ = 25 – 2
=> (sin² θ + cosec² θ) = 23 (Ans.)