CLASS-6
INTRODUCTION OF INTEGERS
INTRODUCTION OF INTEGERS -
Integers are a fundamental concept in mathematics that represents whole numbers, both positive and negative, along with zero. They are used to describe quantities in various contexts, ranging from counting objects to measuring distances. Integers are an essential building block in arithmetic, algebra, and many other areas of mathematics.

The set of integers can be denoted by the symbol ℤ, and it includes the following elements:
............., -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, ..............
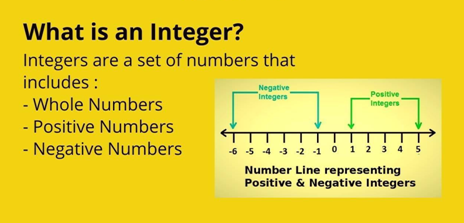
Key Characteristics Of Integers Include:-
- Positive Integers:- These are whole numbers greater than zero. They are often used to represent quantities such as items, money, or positions.
- Negative Integers:- These are whole numbers less than zero. They can represent values below a reference point or indicate debts, losses, or positions in the opposite direction.
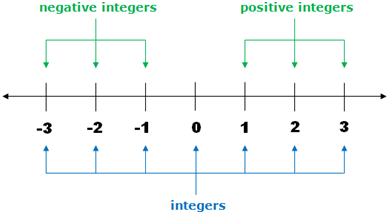
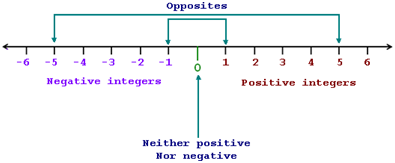
3. Zero:- It is a unique integer that represents the absence of quantity or value. It serves as the neutral point between positive and negative integers on the number line.
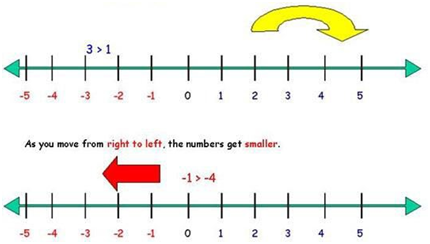
4. Addition and Subtraction:- Integers can be added or subtracted to perform various calculations. Adding a positive integer is equivalent to moving to the right on the number line, while adding a negative integer is equivalent to moving to the left.
5. Ordering:- Integers can be arranged in order on the number line, from least to greatest or vice versa.
6. Arithmetic Operations:- Integers can be involved in arithmetic operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. The result of these operations may be another integer or a rational number (a fraction).
7. Absolute Value:- The absolute value of an integer is its distance from zero on the number line, always yielding a non-negative value.
8. Number Line:- Integers are often represented on a number line, a graphical representation where each integer is placed at a specific